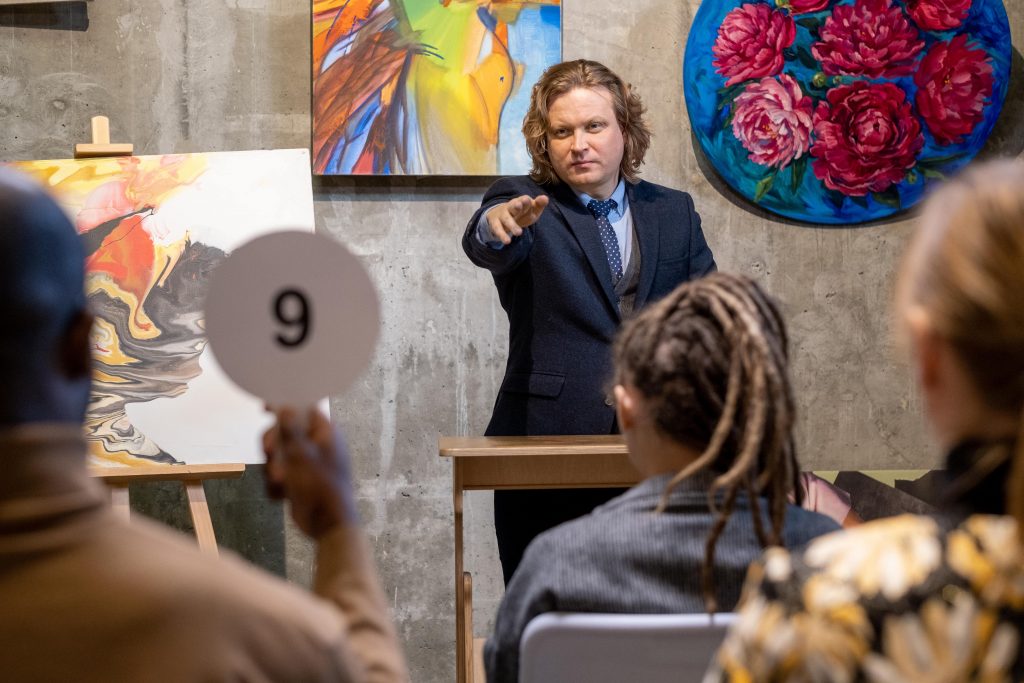
An auction is a sale of property to the highest bidder. It can be done by the seller himself, or through an agent engaged by him. In a typical auction, the auctioneer is paid by the seller based on commission.
The auctioneer has a duty of fairness and competence. He or she must conduct the sale in such a way that will bar fraudulent bidders, and earn the confidence of honest purchasers.
This obligation of the auctioneer is a fiduciary relationship and the law imposes on him a duty to turn over the proceeds of the sale in full. This duty is akin to a trustee’s duty to turn over monies in trust for the benefit of a particular beneficiary.
In addition to the responsibility to turn over the proceeds of the sale in a full and satisfactory manner, an auctioneer also has a responsibility to disclose to bidders his or her personal valuation of the goods being sold. This disclosure is intended to encourage bidders to reveal their valuations, discourage cheating and collusion by encouraging them to be truthful in their bidding, and to maximize revenues from the sale of the goods.
If a person sells something at an auction, the title to that thing will pass upon the falling of the gavel or another action by the auctioneer that constitutes an acceptance of a bid. However, the title may be subject to an express condition that prevents it from passing until the condition is met.
Often, an auctioneer will rescind the sale of a piece of property in the event of a failure on the part of the bidder to pay the bid price or comply with the terms and conditions of the purchase. In these cases, the auctioneer cannot rescind the sale without the seller’s express consent.
The buyer’s rights and obligations in an auction are governed by the general principles of agency law. This means that the buyer is an agent of the seller and that the seller can compel the auctioneer to act in a certain way by giving him or her a statute to that effect.
There are several types of auctions. These include public, first-price, sealed-bid and private sales. In the latter, bidders submit bids in sealed envelopes and the highest bidder receives the object at that bid price.
In the United States, a bidder has a right to rescind the sale of an item by giving written notice to the auctioneer within the time limit set forth in the governing statute. This notice must be in writing and signed by the bidder.
If a bidder fails to deliver a notice of rescindment before the date of the auction, the auctioneer must return the deposit made by the bidder. The deposit may be a cashier’s check or a certified check.
The auctioneer is a legitimate business and his or her conduct of the sale is lawful, provided reasonable regulations are complied with. Moreover, the auctioneer’s bond is a defense in the case of a suit for breach of contract.